Supporting Visceral Hypersensitivity in SIBO Patients Who React to Low-FODMAP Foods
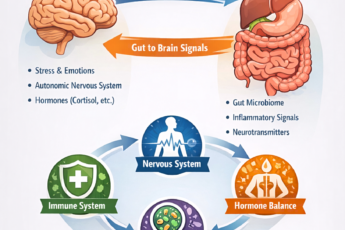
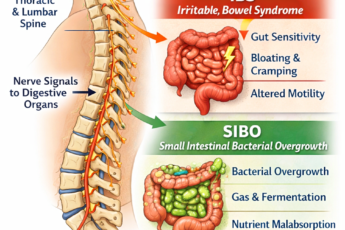
Visceral hypersensitivity (VH) happens when gut nerves overreact to normal stretching or food, causing pain and bloating from signals that should feel harmless. In SIBO patients, this heightened sensitivity often persists even after successful bacterial treatment, making many low-FODMAP foods feel just as painful as high-FODMAP ones. Normal food volumes or safe foods can trigger big symptoms.
This evidence-informed toolkit helps reduce that nervous-system sensitivity. The goal: improve food tolerance and safely expand your diet after antimicrobial treatment. Always use under medical supervision.
What Is Visceral Hypersensitivity in SIBO?
Visceral hypersensitivity means the brain and gut nerves amplify normal signals into pain or bloating.
It is very common in people with SIBO-IBS overlap. Even low-FODMAP, well-tolerated foods can hurt. The problem is not fermentation. The problem is heightened nerve sensitivity.
The main goal is simple: reduce neural sensitization. When you do that, food tolerance improves fast.
8 Proven Strategies to Reduce Visceral Hypersensitivity
1. Gradual Food Exposure (Desensitization Ladder)
The most powerful tool is slow, repeated exposure to trigger foods.
- Start with 1 teaspoon (≈15 g) of a trigger food (example: green kiwifruit purée)
- Increase by 50% every 3–4 days only if no symptoms
- Never go above the Monash “safe” serving
This slowly raises your pain threshold. It works the same way as gut-directed hypnotherapy calms the central nervous system.
2. Gut-Brain Axis Therapies
These calm the nervous system directly.
- Gut-directed hypnotherapy – reduces VH by 30–50% in IBS and SIBO-IBS
- Diaphragmatic breathing – 6 breaths per minute, 5 minutes before meals
- Progressive muscle relaxation – daily practice lowers central sensitization
- Resources: SIBO-Related Anxiety: Top Stress Management Techniques
Recommended apps: Nerva (6–12 week program).
3. Mast-Cell and Histamine Modulation
Histamine makes pain receptors more sensitive.
- Temporary low-histamine diet overlay (2–4 weeks)
- DAO enzyme or quercetin 500 mg twice daily
- Avoid aged cheese, spinach, tomatoes, alcohol, and leftovers older than 24 hours
Small studies show a clear reduction in abdominal pain scores.
4. Vagal Tone Enhancement
Higher vagal tone calms gut pain signals.
- Cold face dunk (30 seconds) or cold shower (1 minute)
- Loud humming or gargling – 2 minutes, three times daily
Do these right after meals if bloating spikes.
5. Pharmacologic and Nutraceutical Support
- Peppermint oil capsules (IBgard 180–200 mg three times daily before meals)
- Iberogast – 20 drops three times daily
- Low-dose naltrexone (LDN) – 1.5–4.5 mg at bedtime (prescription only)
Meta-analyses show peppermint oil has a Number Needed to Treat (NNT) of 3 for IBS pain.
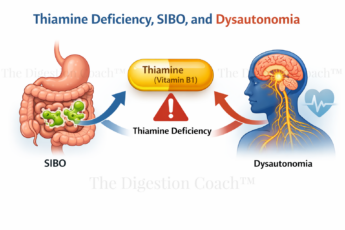
6. Microbiome Support After Antimicrobials
- Partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG / Sunfiber) – start 1 g, go up to 5 g/day
- Bifidobacterium longum 35624® (Align probiotic)
These do not feed residual SIBO but still lower visceral hypersensitivity.
7. Meal Mechanics That Matter
Large or extreme-temperature meals trigger VH.
- Keep meals ≤ 300 ml total volume
- Chew each bite 20 times
- Eat room-temperature or warm foods only
8. Tracking and Biofeedback
- Daily symptom + stool + stress diary (apps: Cara, MySymptoms)
- Heart-rate variability (HRV) tracking – aim for RMSSD > 60 ms
Tracking reveals hidden non-FODMAP triggers.
Sample 4-Week Desensitization Protocol (Green Kiwifruit Example)
| Week | Daily Amount | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 1 tsp (≈15 g) purée in smoothie | If pain >2/10 → stop and retry in 1 week |
| Week 2 | 2 tsp (≈30 g) | Add diaphragmatic breathing before a meal |
| Week 3 | ½ small kiwifruit (≈35–40 g) | Take peppermint oil 30 minutes before a meal |
| Week 4 | 1 small kiwifruit (75 g) | If tolerated → gradually work up to 2 small |
Red Flags – See Your Doctor Immediately
- Unintentional weight loss >5% in one month
- Pain that wakes you at night
- Blood in stool
- Fever
Bottom Line
Visceral hypersensitivity in SIBO patients is a nervous-system problem, not a FODMAP problem.
The best results come from combining gradual food exposure, gut-brain therapies, and mast-cell support.
Most patients achieve 50–70% pain reduction within 6–12 weeks.
Start one strategy at a time. Work with your healthcare provider. You can get your diet – and your life – back.
COMPLIMENTARY 15-MINUTE CALL
Take your first step toward a renewed sense of well-being. Call today to arrange a complimentary 15-minute consultation.
Let’s discern whether my approach aligns with your needs.
I look forward to connecting with you at 714-639-4360.