The Sunlight-Gut-Brain Axis: How Light, Nitric Oxide, and Redox Biology Govern Human Health
Modern life hides us from the sun—and our biology is paying the price. Most people know sunlight helps produce vitamin D. But did you know that light also controls how well your gut barrier functions, how strong your brain’s blood vessels are, and how much energy your mitochondria can make? Let me explain how the sunlight-gut-brain connection operates through the lens of redox health, redox biology, nitric oxide, and circadian rhythm.
Table of Contents
- What Is the Redox System and Why Does It Matter?
- How Does Sunlight Improve Mitochondrial Function?
- What Happens in the Gut When Redox Power Drops?
- Why Do Brain Bleeds and Gut Problems Often Happen Together?
- How Does Light Reset the Circadian Clock?
- How Does Nitric Oxide Work With Light?
- Evolution Proves Sunlight Is Essential
- What Can You Do to Rebuild Redox Health?
- Final Takeaway: Light Is the First Nutrient
What Is the Redox System and Why Does It Matter?
Redox balance is your body’s mechanism for regulating energy production and controlling inflammation.
- Redox stands for reduction–oxidation reactions, which transfer electrons in your cells.
- Your mitochondria use these reactions to make ATP, the energy currency of life.
- A good redox state is characterized by strong energy production and low inflammation.
When redox balance is off, mitochondria fail. That leads to gut leakiness, brain inflammation, and chronic disease.
How Does Sunlight Improve Mitochondrial Function?
Sunlight powers mitochondria in a surprising way—it helps release nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Nitric oxide (NO) dilates blood vessels and boosts oxygen delivery.
- Blue and UV light trigger NO release through melanopsin, a light-sensitive protein found in the eye.
- Local NO tells cells to temporarily lower ATP production and make ROS instead.
ROS serve as stress signals. They reset the redox balance and can emit biophotons—light produced within cells.
What Happens in the Gut When Redox Power Drops?
The gut lining is electrified by mitochondrial ATP. It powers tight junctions that prevent pathogens from entering.
When redox drops:
- Cells lose charge
- Tight junctions break down
- Bacteria and toxins leak into the bloodstream
This is leaky gut syndrome.
Without sunlight, NO levels drop, oxygen falls, and the mitochondria fail—leading to dysbiosis and inflammation.
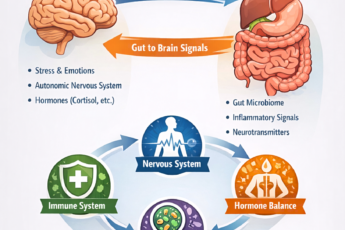
Why Do Brain Bleeds and Gut Problems Often Happen Together?
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) patients often show gut inflammation.
- Both tissues rely on strong mitochondrial power.
- Both collapse when redox fails.
- Sunlight loss weakens vessel walls and gut junctions.
This distant-light impact is called the abscopal effect.
How Does Light Reset the Circadian Clock?
Circadian rhythms regulate sleep, hormones, and gut motility.
- Sunlight is the primary reset signal.
- It acts through proteins such as PER2 and HIF-1α.
- These also regulate redox balance and mitochondria.
Without light, you drift out of sync—leading to insomnia, IBS, and immune dysregulation.
How Does Nitric Oxide Work With Light?
Nitric oxide (NO) is a short-lived gas with big biological effects.
- Acts locally and quickly
- Triggers vasodilation
- Modulates ATP and ROS output
UV and blue light stimulate the production of NO, which affects cellular redox and light emission—connecting biology to quantum effects, such as magnetochemistry.
Evolution Proves Sunlight Is Essential
After the KT extinction, 66 million years ago, mammals survived by adapting to low-light stress via mitochondrial pathways.
Today, we’re chronically light-deprived—and it shows in our disease patterns.
- Heart disease
- Autoimmunity
- Fatigue
- Depression
All share poor mitochondrial redox and insufficient light exposure.
What Can You Do to Rebuild Redox Health?
Restore your light environment to heal gut and brain function.
Morning:
- Sunlight in your eyes within 30 minutes of waking
- Bare skin exposure early in the day
Midday:
- Main meal around solar noon
- Sync gut circadian clocks with the sun
Evening:
- Avoid artificial ‘blue’ light at night (ALAN)
- Use red bulbs or candles
Bonus: Walk barefoot in sunlight to ground and recharge your redox system.
Final Takeaway: Light Is the First Nutrient
Sunlight controls:
- Mitochondria
- Redox balance
- Circadian rhythm
- Gut barrier integrity
- Brain blood flow
Light is the forgotten nutrient. Reintroduce it daily and rebuild your sunlight-gut-brain connection.
Take action: Go outside early, often, and with intention. Your biology will thank you.
Similar Topic: