Microbial Metabolite via Gut-Liver Axis Repairs Damaged Liver
10-hydroxystearic acid (10-HSA), a microbial metabolite for liver repair key player in the gut-liver axis. The gut-liver axis is a vital pathway linking gut health to liver function. Produced by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (LP), this microbial metabolite activates PPARα, a receptor protein that regulates lipid metabolism and reduces liver inflammation, to repair liver damage. This blog explores how 10-HSA, a gut-derived microbial metabolite, supports liver recovery. It also covers substrates needed for its production and ways to boost it naturally. Read on to learn how this microbial metabolite supports the gut-liver connection. Read about other gut axes.
Table of Contents
- What Is the Gut-Liver Axis?
- What Is 10-HSA and How Does It Help the Liver?
- How Does LP Produce 10-HSA?
- How Can You Boost 10-HSA in the Gut?
- Why Is 10-HSA Promising for Liver Health?
- What Are the Challenges and Next Steps?
- Summary and Call to Action
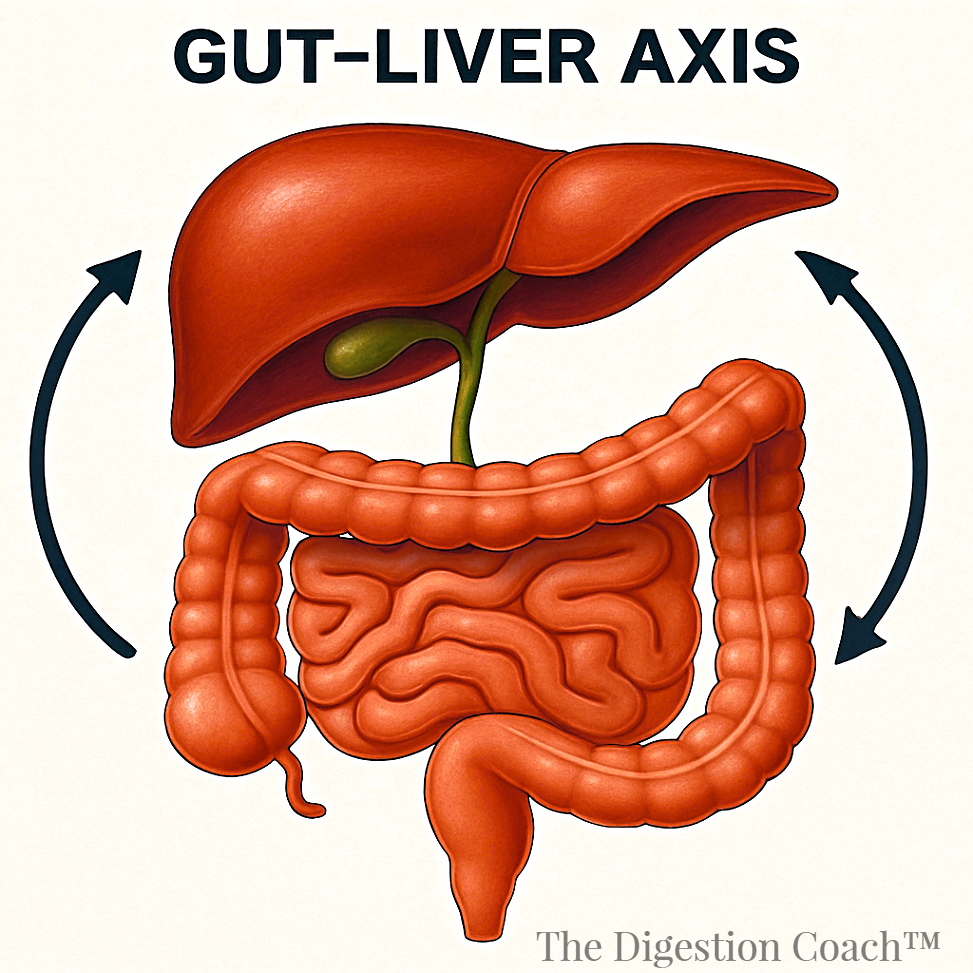
What Is the Gut-Liver Axis?
The gut-liver axis connects the gut and liver through blood flow and signaling. The liver receives nutrients and metabolites from the gut via the portal vein. Gut bacteria, like LP, produce compounds that influence liver health. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiota, can harm the liver. Conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) often stem from poor gut health. Restoring gut balance can support liver repair.
What Is 10-HSA and How Does It Help the Liver?
10-HSA is a microbial metabolite produced by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. It acts as a PPARα agonist, meaning it activates the PPARα receptor, which regulates lipid metabolism. This reduces liver fat buildup and inflammation. In mouse studies, 10-HSA reversed NAFLD damage. It also repaired gut barriers, preventing toxins from reaching the liver. Unlike synthetic drugs, 10-HSA has no known toxic effects.
How Does LP Produce 10-HSA?
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum converts specific substrates into 10-HSA. The process relies on dietary fats and microbial enzymes. Here are the key substrates:
- Oleic Acid: Found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts. LP utilizes oleate hydratase to add a hydroxyl group, resulting in 10-HSA.
- Linoleic Acid: Present in sunflower and soybean oils. It can be metabolized into 10-HSA or related compounds.
- Enzymatic Support: Oleate hydratase drives the reaction. Anaerobic gut conditions enhance this process.
Without these substrates, 10-HSA production drops. A diet rich in healthy fats supports LP’s activity.
How Can You Boost 10-HSA in the Gut?
Increasing 10-HSA production requires optimizing LP’s environment. Here are practical steps:
- Eat Oleic Acid-Rich Foods: Include olive oil, almonds, and avocados in your daily diet. These provide substrates for 10-HSA.
- Consume Prebiotics: Inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS) feed LP. Find them in garlic, onions, and bananas.
- Use LP Probiotics: Select supplements or fermented foods, such as kimchi, that contain verified LP strains.
- Balance Gut Microbiota: Avoid excessive antibiotics or sugar. A diverse microbiota supports LP growth.
- Add Polyphenols: Green tea or berries may enhance LP’s enzyme activity, though evidence is limited.
These steps increase LP’s ability to produce 10-HSA, supporting liver repair via the gut-liver axis.
Why Is 10-HSA Promising for Gut-Liver Axis Health?
10-HSA’s PPARα activation reduces liver fat and inflammation. It outperforms synthetic agonists in safety. Mouse studies show it reverses NAFLD and aflatoxin B1-induced damage. It also strengthens gut barriers, reducing the leakage of toxins to the liver. Human trials are limited, but 10-HSA’s natural origin makes it a promising biotherapeutic. Unlike probiotics, which often yield inconsistent results, 10-HSA offers targeted benefits.
What Are the Challenges and Next Steps?
Not all LP strains produce 10-HSA efficiently. Strain-specific differences matter. Human studies are scarce, relying mostly on animal models. Individual gut microbiota varies, affecting 10-HSA output. Future research should focus on:
- Identifying high-performing LP strains.
- Conducting human clinical trials.
- Developing 10-HSA supplements for precise delivery.
Until then, dietary and probiotic strategies remain the best approach.
Summary and Call to Action
10-HSA, a microbial metabolite, supports liver repair through the gut-liver axis. Produced by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, it activates PPARα to reduce liver fat and inflammation. To boost 10-HSA, eat oleic acid-rich foods, take LP probiotics, and support gut health. While promising, more human studies are needed. Start by adding olive oil and fermented foods to your diet.
COMPLIMENTARY 15-MINUTE CALL
Take your first step toward a renewed sense of well-being. Call today to arrange a complimentary 15-minute consultation.
Let’s discern whether my approach aligns with your needs.
I look forward to connecting with you at 714-639-4360.