Small Intestine
The www.digestioncoach.com category “SMALL INTESTINE” has SMALL INTESTINE-related posts, science-backed articles, protocols, data, information, ideas, thoughts, news, etc.
The small intestine is a tube-shaped organ in the digestive system that absorbs nutrients and water from food:
Function
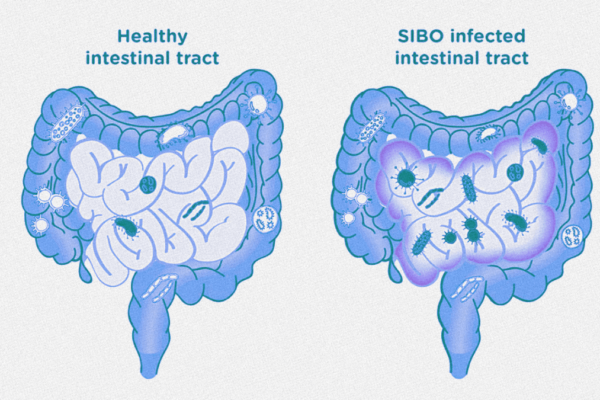
The small intestine is responsible for digesting food and absorbing nutrients and water. It’s the longest part of the digestive tract, measuring about 20 feet long and folded many times to fit in the abdomen.
Parts
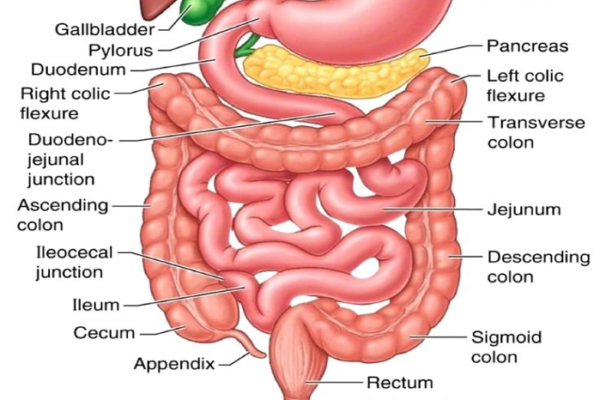
There are three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Structure
The small intestine has a lining of finger-shaped tissues called villi that increase the surface area for absorbing nutrients.
Taste receptors
The duodenum and jejunum contain taste receptor cells that sense sweet, umami, and bitter tastes. These cells may help with nutrient sensing and gut-brain signaling.
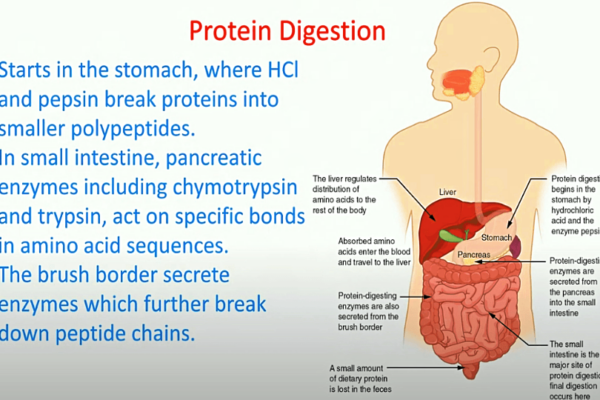
Digestive enzymes and bile
The duodenum receives pancreatic enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver and gallbladder to aid digestion and absorption.
Peristalsis
Rhythmic muscular contractions called peristalsis churn food and mix it with intestinal secretions to aid digestion and absorption.
Ileocecal valve
The ileocecal valve in the ileum passes digested material into the large intestine.